6.5 Creating a Path Rule
Create
a path rule to prevent users from executing applications in a path you
specify. If you create a path rule for an application and intend to
prevent the program from running by setting the security level to
Disallowed, note that a user can still run the software by copying it
to another location. Environment variables, such as %Programfiles% or %Systemroot%,
can be used in your path rule. You can also create a registry path rule
for files that are not always installed in specific file folders. The
wildcard characters * and ? are supported in path rules. To prevent
users from executing e-mail attachments, create a path rule for your
e-mail program’s attachment directory that prevents users from running
e-mail attachments.
To create a path rule, complete the following steps:
1. | Access the Group Policy Object Editor console for a GPO.
| 2. | In
the Group Policy Object Editor console, click Computer Configuration,
double-click Windows Settings, double-click Security Settings, and then
double-click Software Restriction Policies.
| 3. | Right-click Additional Rules, and then click New Path Rule.
| 4. | In the New Path Rule dialog box, shown in Figure 4, type a path in the Path box or browse to a file or folder.
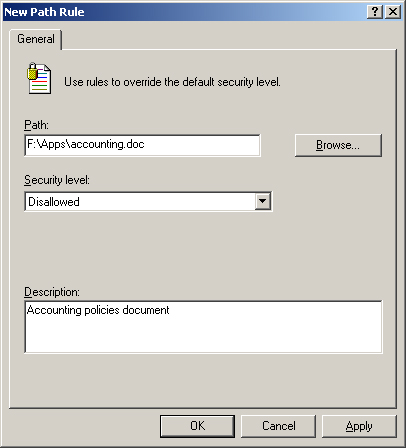
| 5. | In the Security Level list, select one of the following:
Disallowed,
which does not allow the software to run, regardless of the access
rights of the user who is logged on to the computer Unrestricted, which allows software to run with the full rights of the user who is logged on to the computer
| 6. | Type a description for this rule, and then click OK.
|
Important For
certain folders, such as the Windows folder, setting the security level
to Disallowed can adversely affect the operation of your operating
system. Make sure that you do not disallow a crucial component of the
operating system or one of its dependent programs. |
To create a registry path rule, complete the following steps:
Note You must be an administrator to create a registry path rule. |
1. | Click Start, point to Run, type regedit, and then click OK.
| 2. | Right-click
the registry key for which you want to create a rule, and click Copy
Key Name. Make a note of the Value name located in the details pane.
| 3. | Access the Group Policy Object Editor console for a GPO.
| 4. | In
the Group Policy Object Editor console, click Computer Configuration,
double-click Windows Settings, double-click Security Settings, and then
double-click Software Restriction Policies.
| 5. | Right-click Additional rules, and then click New Path Rule.
| 6. | In the New Path Rule dialog box, paste the registry path in the Path box. The registry path should be formatted as follows: %[Registry Hivel]\[Registry Key Name]\Value Name]%.
Notice that the registry path is enclosed in percent (%) signs. The
registry path rule can contain a suffix after the closing percent sign,
for example,
%HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Shell
Folders\Cache%OLK* is valid. This registry path rule identifies the
folder that Microsoft Outlook XP uses to store attachments before
launching them.
Note The registry hive must not be abbreviated. For example, HKCU cannot be substituted for HKEY_CURRENT_USER. |
| 7. | In the Security Level list, select one of the following:
Disallowed,
which does not allow the software to run, regardless of the access
rights of the user who is logged on to the computer Unrestricted, which allows software to run with the full rights of the user who is logged on to the computer
| 8. | Type a description for this rule, and then click OK.
|
6.6 Designating File Types
File
types that are affected by hash, certificate, path, and Internet zone
rules must be listed in the Designated File Types setting in the
Software Restriction Policies extension. The list of file types in the
Designated File Types setting is shared by all rules. However, you can
specify different designated files lists for computer policies and for
user policies.
To designate or delete a file type, complete the following steps:
1. | Access the Group Policy Object Editor console for a GPO.
| 2. | In
the Group Policy Object Editor console, click Computer Configuration,
double-click Windows Settings, double-click Security Settings, and then
double-click Software Restriction Policies.
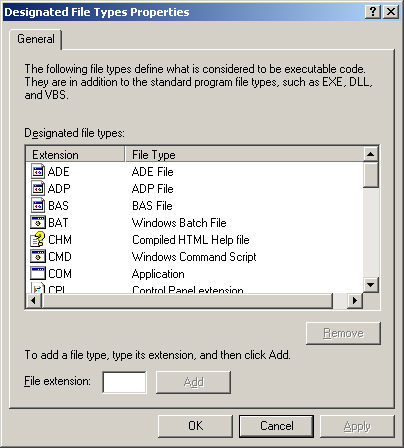
| 3. | In the details pane, double-click the Designated File Types setting.
| 4. | In the Designated File Types Properties dialog box, shown in Figure 5, do one of the following:
To add a file type, type the filename extension in the File Extension box and click Add. Click OK. To delete a file type, select the file type in the Designated File Types list and click Remove. Click OK.
|
|