Executing a Maintenance Plan
Maintenance plans that have been scheduled run
automatically according to the schedule defined. You can also run
maintenance plans manually by right-clicking a maintenance plan and
selecting Execute or by selecting the SQL Server Agent job associated
with the maintenance plan and starting the job. The execution behavior
is different, depending on the means you use. If you choose to run the
maintenance plan from the Management node, the SSIS package is launched, and the Execute Maintenance Plan window displays the current status of the plan execution.
If you run the SQL Server Agent job to execute the
maintenance plan, a dialog box indicating the execution status of the
job appears. The dialog does not indicate success for the maintenance
plan until the entire maintenance plan has completed. The dialog box for
the job can be closed, and the job will still continue to run. The
Execute Maintenance Plan window, on the other hand, does not have an
option to close it, and it must stay open until the plan completes.
There are two other means for monitoring the
execution of maintenance plans. The Job Activity Monitor shows a status
of executing while a maintenance plan is executing. You can set the
refresh settings on the Job Activity Monitor to auto-refresh for the
desired increment. You can also monitor the execution by establishing a
connection to the SSIS server in SSMS. To establish an SSIS connection
in SSMS, you click the Connect drop-down in the Object Explorer and
choose Integration Services. Figure 1 shows an example of the Object Explorer with an Integration Services connection.
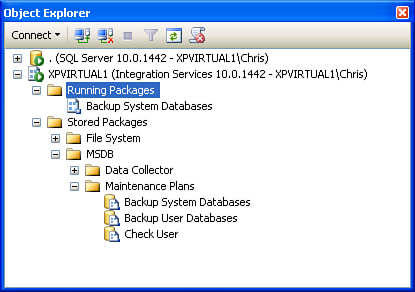
The Integration Services connection in the Object
Explorer shows the packages that are running in addition to the packages
that have been created. If you expand the Stored Packages node and navigate to the MSDB node, you see a node named Maintenance Plans
that shows all the SSIS packages that have been created.
Note
SSIS does not need
to be installed on the SQL Server machine to be able to create and
execute maintenance plans. In the initial release of SQL Server 2005,
this was a requirement but was changed with SQL Server 2005 SP2. This
change carried over to SQL Server 2008, and maintenance plans are now
fully functional with the SQL Server Database Services installation.
Maintenance Without a Maintenance Plan
You can perform database maintenance without the use
of the built-in maintenance plans that come with SQL Server. The
additional complexity in SQL Server 2008 may steer some people away from
the use of these plans. In addition, these plans cannot be scripted, so
deployment to multiple environments is not straightforward.
Database maintenance that is performed without a
maintenance plan is often performed using custom scripts or stored
procedures that execute the T-SQL commands to perform the maintenance.
Other methods include manually executing the SQLMAINT utility
to perform various maintenance tasks such as database backups and
consistency checks. Often these maintenance commands or custom scripts
are then scheduled to run on a regular basis by manually setting up jobs
within the SQL Server Agent job scheduler in SQL Server Management
Studio.
Setting up maintenance tasks manually is a
viable option, especially for the more experienced DBA because it
requires additional development work and familiarity with the
maintenance commands and options. However, even the experienced DBA
should consider using maintenance plans because maintenance tasks set up
manually may lack the integration with other SQL Server components that
is offered with the SQL Server 2008 maintenance plans.
Database Maintenance Policies
Policy-Based
Management, a new management feature introduced in SQL Server 2008,
allows you to manage your SQL Server instances through clearly defined
policies, reducing the potential for administrative errors or oversight.
The policy-based framework implements the policies you defined via a
Policy Engine, SQL Server Agent jobs, SQLCLR, DDL triggers, and Service
Broker. You can choose to have the policies you defined be applied or
evaluated against a single server or a group of servers, thus improving
the scalability of monitoring and administration.
Policy-Based Management allows you to prescribe the
way you want your databases maintained, and the system will help ensure
things stay that way. Essentially, Policy-Based Management allows you to
define rules for one or more SQL Servers and evaluate them. The goal of
this feature is to make it easier for you to manage one or more servers
by notifying you when servers are out of compliance with the database
maintenance policies you have defined.
For example, you could define a policy to ensure that
transaction log backups are being performed on the appropriate
intervals on your OLTP databases. Policy-Based Management allows you to
determine when one of your databases is not in compliance with your log
backup policy. You can set up this policy to be evaluated on demand or
via a schedule.