The formatting JSTL tag
library provides tags that ease internationalization and localization of
web applications. This tag library allows displaying a page in
different languages, based on the user's locale. It also allows locale
specific formatting of dates and currency.
The following example illustrates the use of the formatting JSTL tag library:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Format Tag Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<jsp:useBean id="today" class="java.util.Date" />
<fmt:setLocale value="en_US" />
<fmt:bundle basename="ApplicationResources">
<fmt:message key="greeting" />,<br />
<fmt:message key="proposal" />
<fmt:formatNumber type="currency" value="42000" />.<br />
<fmt:message key="offer_ends" />
<fmt:formatDate value="${today}" type="date" dateStyle="full" />.
</fmt:bundle>
<br />
<br />
<fmt:setLocale value="es_ES" />
<fmt:bundle basename="ApplicationResources">
<fmt:message key="greeting" />,<br />
<fmt:message key="proposal" />
<fmt:formatNumber type="currency" value="42000" />.<br />
<fmt:message key="offer_ends" />
<fmt:formatDate value="${today}" type="date" dateStyle="full" />
</fmt:bundle>
</body>
</html>
This page display
basically greets the user, then proceeds to make a proposal (sales
pitch), followed by a price, and an offer end date:
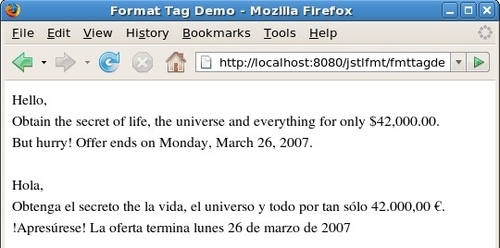
As this page is
internationalized, the actual text of the page is stored in a property
file called a resource bundle. The resource bundle for the page is
called ApplicationResources.properties. This is set in the page via the<fmt:bundle> tag.
The page displays the same
message in English and Spanish. Therefore, two resource bundles are
needed; one for each locale. The locale to use is defined in the value attribute of the<fmt:setLocale> tag.
A real application
would not simultaneously display the same messages in two different
languages. Instead, it would detect the user's locale from the request
and use the appropriate resource bundle. If the user's locale doesn't
match any of the available resource bundles, then the default one would
be used.
The English (and default) version of ApplicationResources.properties looks as follows:
greeting=Hello
proposal=Obtain the secret of life, the universe and everything for only
offer_ends=But hurry! Offer ends on
The Spanish version of the resource bundle is called ApplicationResources_es.properties:
greeting=Hola
proposal=Obtenga el secreto the la vida, el universo y todo por tan sólo
offer_ends=!Apresúrese! La oferta termina
As we can see, a
resource bundle is nothing but a property file with keys and values. The
keys in each localized resource bundle must be the same; the value
should vary according to the locale. In order to be accessible to JSP
pages and Java code, resource bundles need to be placed in any directory
in the WEB-INF/classes directory folder
or any of its subdirectories in the WAR file where the application is
deployed. If they are placed in a subdirectory of the WEB-INF/classes directory, then the basename attribute of the<fmt:bundle> tag must include each directory under this directory, separated by dots. For example, if ApplicationResources.properties and ApplicationResources_es.properties were placed under WEB-INF/classes/ net/ensode, the<fmt:bundle> tag would look like this:
<fmt:bundle basename="net.ensode.ApplicationResources">
As we can see, this looks like a fully qualified class name, but in reality we are pointing to the resource bundle.
Resource bundle names for each locale must have the same base name as the base resource bundle (in this case, ApplicationProperties), followed by an underscore, followed by an appropriate locale (in this case, es). The locale can only specify a language (for example, en or es), or a language and country (for example, en_US or es_ES).
If no country is specified in the locale, any country whose primary
language matches the locale will use the resource bundle for that
language.
The previous example uses es_ES
as the locale, assuming every page that is in Spanish comes from Spain.
Obviously, this wouldn't work in a real application and was done this
way for simplicity.
The<fmt:message> tag looks for a key in the resource bundle matching its key
attribute and displays its value on the page. Although not illustrated
in the example, sometimes resource bundle values can have parameters
that are substituted at runtime with appropriate values. Parameters are
designated by an integer between curly braces. This is illustrated in
the following example:
personalGreeting=Hello {0}
The {0} in this property is a parameter. Parameters can be substituted by the appropriate values at runtime by using the<fmt:param> tag. This tag must be nested inside a<fmt:message> tag. The<fmt:param> tag has an attribute named value. The value of this attribute can be a String
constant or Unified Expression Language expression. It is used to
substitute the parameter with this value. Resource bundle values can
have more than one parameter, in which case, the number of<fmt:param> tags nested inside<fmt:message> must match the number of parameters. The order of the<fmt:param> tags determines which parameter gets substituted. The first<fmt:param> tag will replace the parameter indexed at 0, the second<fmt:param> tag will replace the parameter indexed at 1, and so on and so forth.
The next formatting tag we see in the example is the<fmt:formatNumber>
tag. This tag formats a number according to the locale. Some locales
use a comma to separate thousands and a dot as a decimal separator,
while for others it is the other way around. As can be seen in the
previous screenshot, the<fmt:formatNumber> tag will take care of this for us. Another useful attribute of the<fmt:formatNumber> tag is the type attribute. This attribute has three valid values: number, percent, or currency. As can be seen in the example, if the type attribute is set to currency, then the appropriate currency symbol for the locale is automatically added to the number.
The next new formatting tag we see in the example is the<fmt:formatDate> tag. This tag will take a Date object specified by its value
attribute and format it appropriately for the given locale. In addition
to translating the date into the appropriate language, this tag will
place the day of the week, the day of the month, the month, and the year
in the appropriate place for the corresponding locale. It will also use
the correct capitalization for the first letter of the month. The dateStyle attribute of the<fmt:formatDate> tag has the following valid values: full, long, medium, short, and default. If no value is specified, default is used.
The format tag library tags
we have covered so far are the most commonly used tags. The following
table lists all the JSTL formatting library tags:
|
Tag
|
Description
|
Example
|
|---|
|
<fmt:bundle>
|
Loads a resource bundle to be used inside its body.
|
<fmt:bundle basename="resbund">
<fmt:message key="greeting">
</fmt:bundle>
|
|
<fmt:formatDate>
|
Formats the date specified by its value attribute optionally using a specified pattern.
|
<fmt:formatDate value="${today}" pattern= "MM/dd/yyyy"/>
|
|
<fmt:formatNumber>
|
Formats the number specified by its value
attribute according to the current locale. Can be used to format the
number as currency or percentage, depending on the value of its optional type attribute.
|
<fmt:formatNumber value="42000" />
|
|
<fmt:message>
|
Displays a localized message corresponding to the key defined in its key attribute.
|
<fmt:message key="offer_ends" />
|
|
<fmt:param>
|
Substitutes a parameter in the enclosing<fmt:message> tag.
|
<fmt:param value="someVal"/>
|
|
<fmt:parseDate>
|
Parses a string containing a date into a Date object.
|
<fmt:parseDate value="03/31/2007" pattern= "MM/dd/yyyy" var="parsedDate"/>
|
|
<fmt:parseNumber>
|
Parses a numeric string into a Long or Double object.
|
<fmt:parseNumber value="42,000.00" var= "parsedNumber"/>
|
|
<fmt:requestEncoding>
|
Sets the character encoding of the request.
|
<fmt:requestEncoding key="ISO-8859-1"/>
|
|
<fmt:setBundle>
|
Sets the resource bundle to use in the specified scope. Default scope is page.
|
<fmt:setBundle baseName="resbund" var="bundle" scope="session"/>
|
|
<fmt:setLocale>
|
Sets the locale to use in the specified scope. Default scope is page.
|
<fmt:setLocale value="en_US" />
|
|
<fmt:setTimeZone>
|
Sets the time zone to use in the specified scope. Default scope is page.
|
<fmt:setTimeZone value="EST" var= "sessionTimeZone" scope="session"/>
|
|
<fmt:timeZone>
|
Sets the time zone to use inside its body.
|
<fmt:timeZone value="EST">
<fmt:formatDate value="${today}"/>
</fmt:timeZone>
|