The installation process and
architecture for many of Microsoft’s new products that have been or will
be released in the upcoming years are completely modularized like
Internet Information Services 7.5 on Windows Server 2008 R2. By
providing a modularized approach, web administrators have complete
control over the footprint of IIS when customizing the installation.
This results in the surface area being reduced, which, in turn,
drastically minimizes the chances of a security compromise.
Note
As part of the Microsoft
Trustworthy security campaign, IIS is not installed on Windows Server
2008 R2 by default. You have to add the Web Server (IIS) role via Server
Manager if you want IIS installed.
Before installing or upgrading Internet Information
Services, it is a best practice to fully understand the new modular
installation process, including the features associated with the
installation.
Understanding the
Modular Approach to Installing IIS 7.5
The new buzzword
for Internet Information Services 7.5 modularized installation process
is “slim and efficient.” The modular setup is made up of more than 40
separate feature modules allowing for complete customization when
deploying IIS 7.5. This typically results in minimal surface area and
more granularity compared with older editions of IIS. In addition, even
patching is based on a component level. All of this translates to a
customized footprint for each organization running IIS 7.5.
As illustrated in Figure 1,
the modules, also known as “role services” or “components,” that can be
selected during the installation process of the Web Server (IIS) role
consist of the following:
Web Server
Management Tools
FTP Server
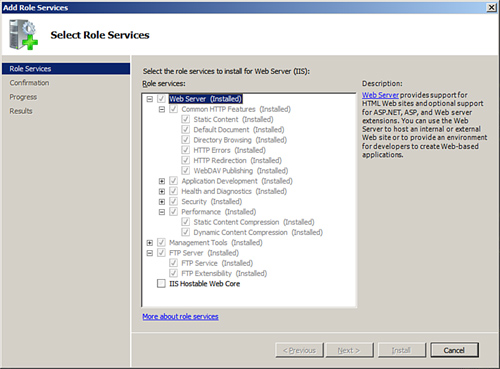
The following sections
depict the modular role services, including an explanation for each.
Web Server Modular/Role
Service
The Web Server modular is
the main service role within IIS 7.5. It can be considered the chief
functionality for a web server because it provides the foundation for
supporting websites and provides developers with a foundation for
development. The Web Server role is further broken down into more types
of features, which can be independently installed, which promotes
further customization of the installation:
Common HTTP
Features— A set of features that
allow for static content to be delivered, the creation of customized
HTTP errors, directory browsing, and selection of default documents are
enabled by default. The HTTP Redirection and WebDAV publishing features
are disabled by default.
Application Development— This feature set is not enabled by default during the
installation. If selected, the Application Development role service
makes available features for creating and hosting web applications.
These features include ASP.NET, .NET Extensibility, ASP, CGI, ISAPI
Extensions, ISAPI Filters, and Server-Side Includes.
Health and Diagnostics— Select this feature to install the tools
associated with monitoring, managing, and troubleshooting an IIS
installation. The independent features include HTTP Logging, Logging
Tools, Request Monitor, Tracing, Custom Logging, and ODBC Logging.
Security— The Security role service includes security
features for controlling website authorization based on authentication
alternatives. In addition, it provides the infrastructure for securing
IIS and the websites associated with the installation. The features that
can be selected include Basic Authentication, Windows Authentication,
Digest Authentication, Client Certificate Mapping Authentication, IIS
Client Certificate Mapping Authentications, URL Authorization, Request
Filtering, and IP and Domain Restrictions.
Performance— Performance features such as Static Content
Compression and Dynamic Content Compression bolster website performance
by managing bandwidth and compression.
The next role
service associated with the Web Server (IIS) role installation is
Management Tools. The management tools provide the means of managing and
administering the IIS 7.5 infrastructure. The following bullets explain
the different management tools available for installation:
IIS Management
Console— If selected, the IIS
Management Console feature installs the latest User Interface tool for
managing, administering, monitoring, and securing IIS 7.5. The tool has
been much improved and provides support for both IIS and ASP.NET.
IIS Management Scripts and
Tools— It is now possible to manage all
of the IIS settings and configurations based on automated script
commands. This feature provides the infrastructure that allows IIS to be
managed by scripts. This is great when there is a need to manage many
IIS 7.5 servers within an infrastructure.
Management Service— This feature provides the foundation within the IIS 7.5
infrastructure for remote management.
IIS 6 Management Compatibility— This feature
provides the tools for backward compatibility when managing an IIS 6.0
infrastructure from a Windows Server 2008 system running IIS 7.5. In
addition, it lets IIS 6.0 management scripts run on IIS 7.5.
FTP Server Modular/Role
Service
The next role service is
known as the FTP Server. It provides a reliable method for making files
available for download and also offers a reliable place for users to
upload files if needed. The three FTP features that can be installed are
as follows:
FTP Service— The FTP Service feature provides the
infrastructure for creating and hosting FTP sites within IIS.
FTP Extensibility— This features enables support for custom providers
and ASP.NET/IIS Manager users.
IIS Hostable Web Core
Role Service— The last role service
allows an administrator the potential to write custom code that will
host core IIS functionality in your own application.
Installing the Web
Server (IIS) Role
Now that you understand
the installation process, including the modules, the next step is to
install the Web Server (IIS) role. You must have Local User
Administrator (LUA) security privileges on the Windows Server 2008 R2
system to be able to install IIS. There are two ways to begin the
installation: adding the Web Server (IIS) role via Server Manager or
installing the services via the command line.
To install the Web Server (IIS)
server role using Server Manager, follow these steps:
1. | Click
Start, Administrative Tools, Server Manager. The Server Manager tools
appear.
|
2. | Right-click
Roles in the left pane of Server Manager, then select Add Roles.
|
3. | On the Select Server Roles page, install IIS 7.5 by
selecting Web Server (IIS) in the Roles section, as shown in Figure 2. A
dialog box pops up, informing you about additional features required
for Web Server (IIS). Click Add Required Features, and then click Next.
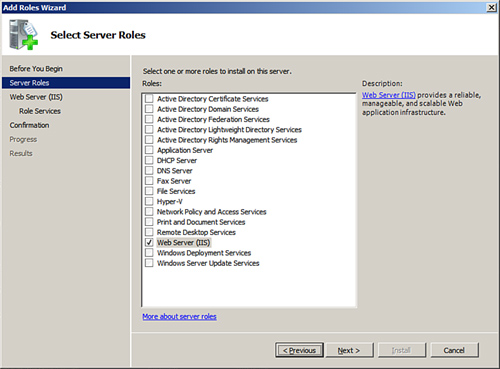
|
4. | Review the
introduction messages and notes on the Web Server (IIS) page, and click
Next.
|
5. | Select the
desired Web Server IIS role services and features to install. The
default settings include Static Content, Default Document, Directory
Browsing, HTTP Errors, HTTP Logging, Request Monitor, Request Filtering,
Static Content Compression, and the IIS Management Console Management
Tool. Click Next. The Confirm Installation Selections page appears.
Note
When installing some of the
IIS components, the wizard warns you that additional services and
features are required as dependencies. Click Add Required Role Services
in the Add Roles Wizard to install the dependencies. These dependencies
might include components of the new Windows Process Activation service.
|
6. | On the Confirm Installation Selections page, review
the roles, services, and features that have been selected for
installation, and then click Install to commence the installation
process.
|
7. | Ensure the
installation succeeded by reviewing the messages on the Installation
Results page, and click Close.
|
Note
After the installation is
complete, additional IIS role services and features can be added or
removed by clicking either Add Role Services or Remove Role Services
within Server Manager based on the Web Server (IIS) role.
Installing the Web
Server (IIS) Role via the Command Line
Windows features and roles
such as IIS 7.5 can be installed using the command line. To install a
default installation of IIS 7.5, run the following script from a
command-line window:
start /w pkgmgr /iu:IIS-WebServerRole;WAS-WindowsActivationService; WAS-ProcessModel;WAS-NetFxEnvironment;WAS-ConfigurationAPI
start /w pkgmgr /iu:IIS-WebServerRole;IIS-WebServer;IIS-CommonHttpFeatures; IIS-StaticContent;IIS-DefaultDocument;IIS-DirectoryBrowsing; IIS-HttpErrors;IIS-HttpRedirect
start /w pkgmgr /iu:IIS-ApplicationDevelopment;IIS-ASPNET; IIS-NetFxExtensibility;IIS-ASP;IIS-CGI;IIS-ISAPIExtensions; IIS-ISAPIFilter;IIS-ServerSideIncludes;IIS-HealthAndDiagnostics; IIS-HttpLogging;IIS-LoggingLibraries;IIS-RequestMonitor;IIS-HttpTracing; IIS-CustomLogging;IIS-ODBCLogging;IIS-Security;IIS-BasicAuthentication
start /w pkgmgr /iu:IIS-WindowsAuthentication;IIS-DigestAuthentication; IIS-ClientCertificateMappingAuthentication; IIS-IISCertificateMappingAuthentication;IIS-URLAuthorization; IIS-RequestFiltering;IIS-IPSecurity
start /w pkgmgr /iu:IIS-Performance;IIS-HttpCompressionStatic; IIS-HttpCompressionDynamic;IIS-WebServerManagementTools; IIS-ManagementConsole;IIS-ManagementScriptingTools; IIS-ManagementService;IIS-IIS6ManagementCompatibility;IIS-Metabase; IIS-WMICompatibility;IIS-LegacyScripts;IIS-LegacySnapIn; IIS-FTPPublishingService;IIS-FTPServer;IIS-FTPManagement; WAS-WindowsActivationService;WAS-ProcessModel;WAS-NetFxEnvironment; WAS-ConfigurationAPI
Upgrading from Other
Versions of IIS
In
many situations, a fresh installation of IIS 7.5 and Windows Server 2008
R2 will not occur because organizations might want to preserve the
existing IIS settings and content. Therefore, organizations must upgrade
their existing IIS infrastructure to IIS 7.5. With the upgrade of the
previous version of Windows to Windows Server 2008 R2, IIS is also
automatically upgraded, allowing web content to be preserved,
translated, and, finally, transitioned. However, you should note early
in the process that Windows Server 2008 R2 only supports a direct
upgrade path from Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2003, which
means only an in-place upgrade from IIS 6.0 or IIS 7.0 is supported.
Likewise, if legacy versions of IIS need upgrading such as IIS 5.0, you
must first upgrade the operating system to Windows Server 2003 and then
to Windows Server 2008.
Note
IIS 7.5 no longer uses a metabase
as in IIS 6.0. The IIS 7.5 XML configuration files replace the legacy
IIS 6.0 metabase.
The upgrade process for IIS is
conducted in three major phases. In the first phase, the new operating
system detects and performs an inventory of IIS components and features
already installed on the operating system. The second phase of the
upgrade process involves upgrading
the legacy operating system to Windows Server 2008 R2. After the Windows
Server 2008 R2 upgrade is complete, the final phase kicks in and
automatically translates the IIS 6.0 metabase information gathered in
the first step, upgrades the legacy IIS metabase to IIS 7.5, and
installs the appropriate IIS 7.5 features.
As is typically the case with
most revised products, Windows Server 2008 R2 IIS is inherently
superior to its previous versions. In particular, it lays claim to being
more secure. This is witnessed during upgrades of websites to IIS 7.5.
Website services are stopped after the upgrade and must be manually
restarted, thus minimizing IIS security vulnerabilities due to previous
Windows defaults. To allow for more clarity, suppose you have a Windows
server with IIS installed, but it isn’t supposed to be serving as a web
server; the server will be more secure by default after you upgrade to
IIS 7.5 because it will not be turned on automatically and made a
subject for attacks.
Another appealing reason for
upgrading from previous versions of IIS is that the IIS 7.5 installation
process is granular and modularized. After upgrading, it is best to
only install the features you require to reduce the surface area
utilized. With that said, be aware that after upgrading to IIS 7.5, a
majority of the web server features are installed right out of the gate
as many legacy versions were not granular.