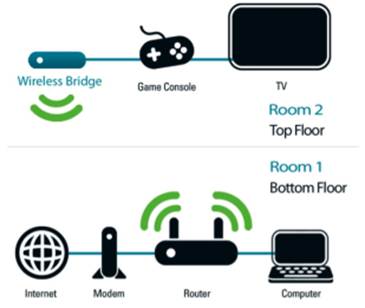
Step 5 - Connecting Wired Devices
With your wired and wireless network map
completed, now it's time to configure your network. Each device on the network
needs to have its own local IP address - a little like a phone number. This IP
address allows the router to know where to send data. If you're playing games
on your Xbox 360, for example, your router needs to know where to send replies
to its data requests. Assigning IP addresses can be done in one of two ways:
automatically or manually. The former uses a protocol called DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol). Configuring this is very easy, as your router will
normally have its DHCP server enabled by default. Each device you connect to
the router is assigned an IP address, which it will retain for a period of
time. You can usually change the lease time (the amount of time that IP address
is reserved for that device) to suit your needs. For the vast majority of home
networks, DHCP means you can add more and more devices to your network without
having to worry about any further configuration.
Sometimes it is advantageous to use a
manual configuration. If the nature of your network is such that you need each
device to always have the same internal IP address - for instance, if you use
it for remote desktop from an externally located PC over the internet, or
stream music from your home network when located elsewhere, it is more sensible
to assign a static IP address. Assigning a static IP address for every device
on a complex network like my own is tedious and not necessary, but I want certain
devices to always have the same IP. I therefore have a static address set from
my desktop PC (for remote desktop) and for my NAS (which I use for remote
streaming and FTP serving). Fortunately, you can use both DHCP and static IP
addresses at the same time. When configuring a static IP address you will need
to input three settings: the Local IP address, the subnet mask and the gateway.
On a windows PC, these are hidden away within the TCP/IP Version 4 settings of
your network adaptor. To keep things simple you should make manually signed IP
addresses variations on a theme. If, for example, your main PC uses the IP
address of 192.168.1.2, use 192.168.1.3 for your NAS, 192.168.1.4 for your
printer and so on. It should be noted that manually assigned IP addresses can
be set outside of the DHCP range of your router; that way you can be sure your
static IP is never assigned to another device. The subnet mask of your network
is defined by the router, but is often 255.255.255.0. Finally, the gateway
should be set to the IP address of your router, which will always be static and
is again defined within the router's settings.
Step 6 - Configuring Your Wireless Network
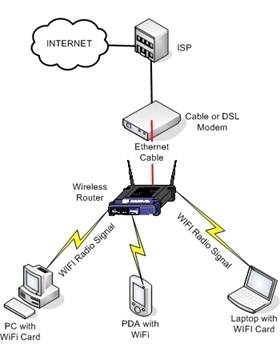
The process for connecting wired and
wireless devices to a network is very similar. Wireless devices are also
assigned IP addresses either manually or dynamically depending on your
preference, but there's an important extra layer to consider: wireless
security. Unless you live in a remote location, you will normally be able to
detect several wireless networks. If you don't have a layer of security in
place, there's nothing preventing someone from connecting to your network and,
at best, leeching off the internet connection you're paying for or, at worst,
compromising the rest of your home network. Fortunately, configuring wireless
security is a doddle. First of all you need to find out what protocol of
wireless security is supported by your devices. If you have a really old laptop
or wireless network adaptor, it may only support WEP. WEP stands for Wired Equivalent
Privacy and was the original encryption standard for wireless. Unfortunately,
WEP keys are relatively easy to compromise, and are not very easy to remember,
as they need to be hexadecimal. WPA is a more secure alternative, and has the
added benefit that you can set the wireless key to an alphanumeric password.
WPA stands for Wi-fi Protected Access, and there are a number of variants. If
all of the devices on your network support it, you should be using WPA2 as your
wireless security protocol of preference, and choose a password that isn't
obvious to crack. Your own name, the name of your house or pet's names are all
on the black list!
Routers, Modems And Switches
Many novice users confuse the terms
'router', 'switch' and 'modem', not helped by the fact that several internet
service providers seem to use the terms interchangeably.
Simply put, a modem is a device that
enables a computer to transmit data over telephone or dedicated data cables.
A router, on the other hand, is a device
that acts as a gateway that can connect two or more networks, which can be
any combination of local area networks (LAN), wide area networks (WANs), or
the internet.
A switch sorts and distributes the
network packets sent between the devices on a LAN.
If you're an ADSL broadband user, then
your router probably contains a modem as well. If you're a cable user, you
usually have a discrete cable modem into which you plug a router.
A modern home broadband router is
actually a multifunction device that combines the capabilities of a router, a
switch, and (usually) a firewall into one box.