The benefits gaining in terms of
performance are estimated at 5% to 10%. The new CPU’s clock rate is not very
promising in favor of speed. Assuming that manufacturing technology does not
changed, the frequency potential of the Haswell CPU might be the same as that
of the Ivy Bridge series.
We used SiSoftware Sandra 2013 SP3, a
synthetic benchmarking suite, testing many aspects relating to different CPU
designs’ performances, and we will make a comparison between the Core i7-4770K
(Haswell) with the quad-core Core i7-3770K (Ivy Bridge) as both of them have
the same clock rate: 3.5 GHz by default and up to 3.9 GHz in the Turbo mode.
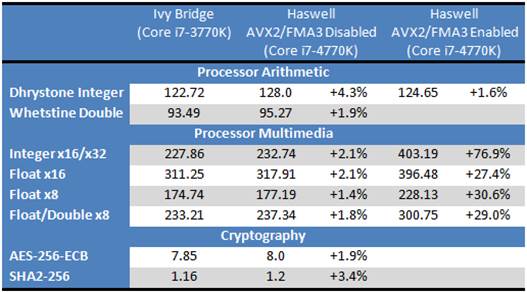
Comparing
the parameters
The result is not encouraging. Unless the
applications use the AVX2/FMA3 (of course, nowadays’ software has not supported
yet), the microarchitecture does not provide any benefit in terms of
performance. It is just 2% - 3% when processing simple Sandra 2013 algorithms
using for benchmarking the performance. Yes, even this improvement should be
appreciated when looking at Intel’s current priorities and the lack of
competition between the top-performance x86 CPUs. If new instructions are
actually implemented everywhere, the Haswell can be much better compared to its
predecessor with a certain increase in performance of 30-40%. It depends on how
current application developers use that advantage.
Well, we can also hope that Haswell would
be somehow faster in practical applications in all of the cases, although there
is no innovation in its microarchitecture can be the basis of this hope, but on
the higher bandwidth of the L1 and L2 cache. This can be easily seen in any
professional benchmark like the Sandra 2013 SP3. The tests are conducted based
on the DDR3-1866 SDRAM platform (9-11-9-27-1T timing).
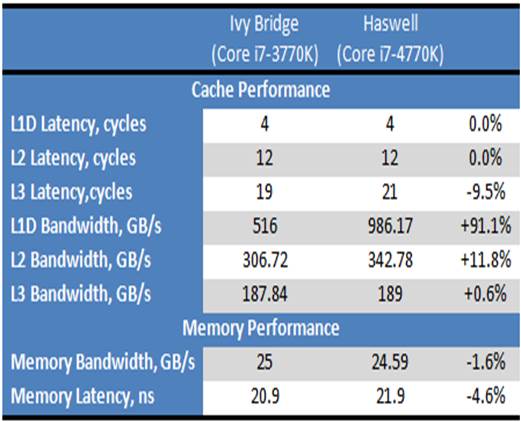
Comparing
the parameters
Therefore, in the Haswell, the L1 and L2
cache seem to operate much faster than that its predecessor. This is a very important
advantage of the microarchitecture which can make it faster compared to the Ivy
Bridge in the practical applications. On the other hand, the L3 cache and
memory controller seem to perform slower, which might affect negatively on the
performance. Enabling individual control over power-saving states of the uncore
part of the CPU, the clock rates of the L3 cache and memory controller are not
connected to the clock rate of the x86 core. Although the subunits works at the
similar frequencies as the x86 cores, their performance would actually lower in
return of the asynchronous operation.
Summing everything up, it is very hard for
the new Haswell microarchitecture to life the performance of Core CPU to a new
level. The only certain thing that all of the new innovations ensure you is
just a minor boost in speed, which is originated mostly from increase of cache
memory bandwidth rather than from any changes in the execution pipeline. Theoretically,
by using the AVX2/FMA3 code, Haswell might display better, but it seems that
the applications do not want to write such code even when some of the
instructions have been supported by AMD processors as well.
Haswell for Desktop in Details
What is introduced under the name of
Haswell is the latest update of the Core architecture. It would be used for all
of the modern desktops manufactured in the next several years, except for the
LGA2011 infrastructure designed for the CPU Sandy Bridge. Actually, there is
not much for Haswell to show off when talking about desktops. This CPU would be
manufactured based on the 22nm facilities using 3D transistors. It also
supports the FMA3/AVX2 code for the latest features and faster L1 and L2 cache,
and provides the certain optimization in favor of parallel execution.
The basic innovation can be easily realized
in the Haswell semiconductor die, which not only look so alike the Ivy Bridge
but also similar in terms of dimensions and configuration.
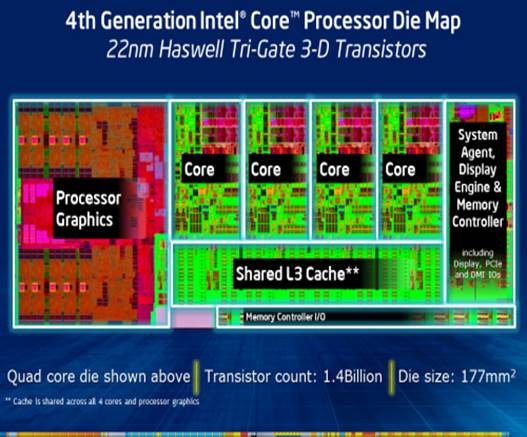
Processor
die map
The quad-core die point of the Haswell
desktop (featuring with the integrated GT2 graphics core) incorporates 1.4
billion transistors and is 177 sq. mm. Its Ivy Bridge counterpart just has
15%.incorporating 1.2 billion transistors (we would like to emphasize the
complexity in the synthetic design that does not looking at some duplications
of certain elements in the die). Half of the transistors list added to be in
charge of the graphics core is now occupying 30% of the whole CPU die, so there
are very few positions left for any change in the microarchitecture of the x86
cores.
As the result, there is no considerable
change in terms of technical details in the new CPUs. The CPU generations still
have the same x86 core number and similar technology. The clock rate and number
of cache memory amounts are not very different. You might notice this in the
specifications that Intel would announce within 3 days.
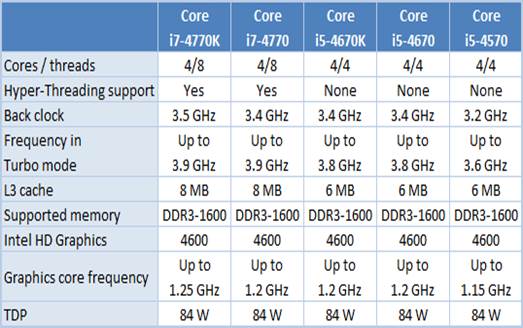
The
parameters
Therefore, the senior desktop Haswell CPUs
have almost the same specifications as the senior products of the previous
generation. That is why no performance benefit seems to be possible to us
thanks to the higher clock rates or larger cache. There are only two
differences. First, the obviously faster graphics core of the Haswell desktops
than that of Ivy Bridge is just because there are more execution devices in it.
Second, the increase of 77-84 watt of TDP is because some voltage regulator
components have been moved to the CPU die.
The Core i7 series distinguish from the
Core i5 series in the same way as before. Both of the series include the CPU
quad-cores but Hyper-Threading is supported by Core i7 series, and the topmost
model in each series is still an overclockable K-indexed with unlocked
multipliers. However, there is no more offers of different graphics cores from
Intel in its new quad-core CPUs now, so all of them use mainly the GT2 core
with 20 executive devices. The graphics core GT1 might be limited to junior CPU
series.
There is almost no difference in the price
policy. $10 would be the maximum price gap between similar CPUs of different
generations.
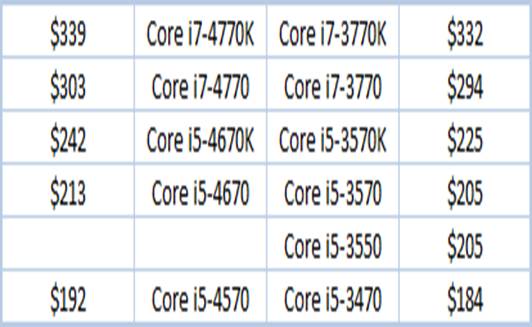
Comparing
price
We should also add that we do not describe
the whole Haswell desktops series here. Intel is really preparing for its
unusual biggest release to introduce, beside the Core i7 and Core i5 for
regular computer, the dedicate CPU version with S index (with the TDP 45 or 35
watt) and R index (in BGA package coming with the GT3 Iris graphics core). We
will discuss more details in our upcoming reviews.