PC
Greater flash memory – 1 terabyte SSDs

Solid State Drives will be bigger than ever in
2012. Various manufactures – Seagate, MemoRight and SanDisk for example – have
announced flash memory with a capacity of up to 800GB. With the Octane series,
OCZ Technology is going for 1TB SSDs, which costs about $1795. With the new
disks, manufacturers are targeting a turnover of one billion US dollars in the
server market in 2012, and 4 billion in 2015. The 2.5 and 3.5-inch drives are
also suitable for normal desktop PCs. Private users who can afford to dabble in
the love of hardware can make the splurge. These Mega-SSDs, however, are not
suitable for notebooks simply for being too thick.

Graphics cards – more performance, less
consumption
They heat up quickly, ventilate loudly
and consume too much electricity – this is how current generation of graphic
cards are, and they’re running on limits. The upcoming card from NVIDIA and AMD
are not upgrades of a prevailing hardware, but a completely new architecture.
The most important innovation from both manufacturers are the reduced GPUs,
going from 40 to 28 nanometres. Whereas the Kepler card planned by NVIDIA are
hardly known just yet, details on the Radeon HD-7,000 series from AMD have
already been leaked. AMD’s flagships, the HD 7970 and the 7950, are getting the
more energy-saving 2GB XDR2 memory instead of GDDR5. The XDR2 memory runs with
a clock frequency of up to 8,000MHz. Combined with the smaller feature size of
the GPU, the cards consume less energy but are able to provide higher
performance. For comparison, the HD 7970 (codenamed Tahixi XT) should require a
maximum of 190 watts, while the HD 6970 consumes a full 250 watts. Following
this, a new range of graphic cards with dual CPU is also coming to the market,
falling within the PCIe specification of 375 watts – current cards can hardly
adhere to this limit.
AMD’s
new high-end-graphics
The AMD Radeon HD 7970 is about 3D
percent quicker and , in spite of this, is still more energy-saving than its
forerunner model HD 6970.
GPU

|
|
HD 6970 (alt)
|
HD 7970 (neu)
|
|
Name
|
Cayman XT
|
Tahiti XT
|
|
Size
|
40 mm
|
28 mm
|
|
Cluster
|
24
|
32
|
|
Cores
|
1.536
|
2.048
|
|
Billing increment
|
880 MHz
|
1.000 MHz
|
Memory
|
|
HD 6970 (alt)
|
HD 7970 (neu)
|
|
Architecture
|
GDDR5
|
XDR2
|
|
Size
|
2 GB
|
2 GB
|
|
Billing increment
|
5,500 MHz
|
8,000 MHz
|
|
Bandwidth
|
176 GB/s
|
256 GB/s
|
|
Performance
|
250 W
|
190 W
|
HDD
hard disks – 5 terabytes for PCs

While SSDs are certainly on the way
up, standard hard disk drives wouldn’t be extinct for a long time. On the
contrary, 2012 would be where they will experience growth. Seagate has
announced to present the first HDD with a capacity of 5 terabytes in January
(the Icon). Five single disks are embedded in each TB. Other manufacturers have
even announced 4TB models – internal ones as well as external – for 2012. The
great advantage of HDDs against SSDs is the price: while the 1TB SSD cost as
much as $1795, a customer would only need to pay about $80 for a HDD of the same
capacity. This ratio isn’t going to change in the future, though the prices for
both models are going to reduce in price further in the future.
SATA express – New Connection for
Superfast SSDs
HDDs have been bottlenecked on PCs for
too long. Thanks to SSDs, things still hasn’t changed. The latest generation of
SSDs on flash-basis has reached the limits of SATA technology, but have they?
What if we told you that while SSDs can reach 600MB/sec, SATA could go for
6GB/sec? There has been faster devices out there, but for them to work
optimally, the drives must be connected to the considerably faster PCIe-slot –
something that requires a specific drive and does not run error-free all the
time. The Serial ATA International Organisation (SATA-IO) will publish a new
connectivity standard, known as the SATA Express, to rectify this problem. SSDs
can transfer their data via PCI Express 3.0 without any further adaptors
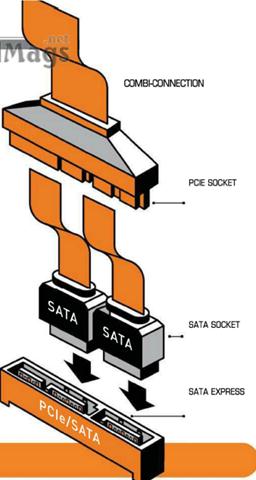
through this interface. Two versions of the motherboard sockets are being
planned: the first one provides the connection only via PCIe cable, while the
second one shall be compatible with the older SATA disks (see picture).
Motherboard manufacturers will determine which version should be used. The
SATA-IO sets the transfer rate of SATA express at 8GB and 16GB, meaning the
actual transfer rate may be 1GB/sec or 2GB/sec. the first motherboards with the
new SATA Express connectivity should arrive into the market by mid-2012.
Combi-Connection
SATA Express uses the PCIe interface
for data transfer – hence, a transfer rate of up to 16 GB/sec should be
possible.
PCIE
Socket
New socket for boards and SSDs which
connects via SATA Express
SATA
Socket
The old sockets also fit in the new
connection
SATA
Express
New mainboards should have
connections compatible to SATA
Ivy Bridge
Tri-Gate – 3D Processors?
The
3D buzzword will also hit
processors in 2012 as Intel will be delivering the first Ivy Bridge
chips with three-dimensional transistors, known as Tri-Gate. The reason
for the
seemingly strange name is a component of the transistors, the channel,
which
will now protrude out from the otherwise flat layer. Tri-Gate processors
work
more efficiently with the same size. Due to its perpendicular structure,
the
channel prevents the electricity from flowing through the transistor
even when
switched off. Up to now, such current leaks were prevented by processors
of
smaller structures. This is because Tri-Gate transistors are only 22
nanometres
wide and hence 10 nanometres slimmer than the current Sandy Bridge
processors, and as thus, more transistors can be accommodated in the
same amount of
space. Intel can use this technology in two ways: either increase the
number of
transistors in the Ivy Bridge CPUs, resulting in increased performances
by 50%,
or let the processor save 40% more energy while working with the same
number of
transistors, as there are hardly any electrical leaks. Lastly, it will
interesting for mobile devices when a more performing version is used on
the PC
motherboards. Here, the power supplies are strong enough for more
consumption.