The
transport pipeline reflects the internal routing of messages within the
Hub Transport server. The elements of this are shown in Figure 17.10. These consist of the following:
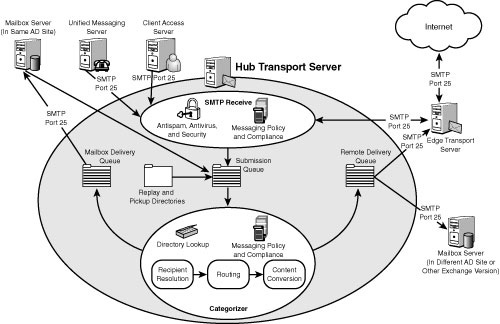
The figure also illustrates the relationships that the Hub Transport server role has with the other Exchange Server 2010 roles.
Messages get into the transport pipeline onto a Hub Transport server through one of four ways, as shown in Figure 17.10:
Through the SMTP Receive Connector
Through files being placed in the pickup or replay directories
Through the submission queue by the mailbox store driver
Through submission from an agent (not shown)
After the messages
have gotten into the pipeline, they flow through the pipeline. The
various segments of that pipeline are discussed in the following
sections.
SMTP Receive Connector
In the Hub
Transport server, the SMTP Receive Connector accepts SMTP (port 25)
messages. Basic server-level policies are applied, such as the
authorization of the remote IP address of the server and authentication
of the server.
If installed on the Hub
Transport server, the messages coming into the SMTP Receive Connector
are also processed by antivirus and antispam services.
If they pass the SMTP Receive Connector, the messages flow down the transport pipeline to the submission queue.
Submission Queue
The
submission queue takes messages from the SMTP Receive Connector, as
well as from the mailbox store driver, the pickup and replay
directories, and from agents such as the transport rules agent.
When messages enter the submission queue, the OnSubmittedMessage event activates. This triggers the journaling agent.
The messages are held in the submission queue until they are pulled out one at a time (first in, first out) by the categorizer.
Categorizer
The categorizer processes each message that it retrieves from the submission queue. The categorizer does four main steps:
- Resolving recipient addressing
- Determining routes to recipients
- Converting message content
- Rules processing
The last step, rule processing, is where the agents that trigger on the OnRoutedMessage
event activate. On the Hub Transport server, that is all the default
agents, including the rules transport agent, the journaling agent, and
the AD RMS Prelicensing agent.
Mailbox Delivery Queue
The mailbox delivery
queue handles messages that are destined for local delivery—that is,
messages for recipients in mailbox servers in the same site as the Hub
Transport server.
These messages are pulled off the queue one by one and delivered to the user’s mailbox by the store driver.
Remote Delivery Queue
The remote
delivery queue handles messages to be routed to other Hub Transport
servers within the forest for messages destined for other mailbox
servers within the organization but in a different AD site. The remote
delivery queue also handles messages destined for external mail systems
in other forests and for the Edge Transport servers.
Messages in the remote delivery queue are sent out via the SMTP Send Connector.