LTE, with its
spectrum flexibility, has a good life ahead since it can be accommodated into
many different swathes of spectrum. It uses wider chunks of spectrum, allowing
nearly four times faster data transfer than 3G.
Long Term Evolution (LTE) is a 3GPP
standard that provides uplink speed of up to 50 megabits per second (Mbps) and
downlink speed of up to 100 Mbps. The 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project)
unites telecommunications standards bodies, and provides their members with a
stable environment to produce successful reports and specifications that define
3GPP technologies such as LTE - a major advance in cellular technology.
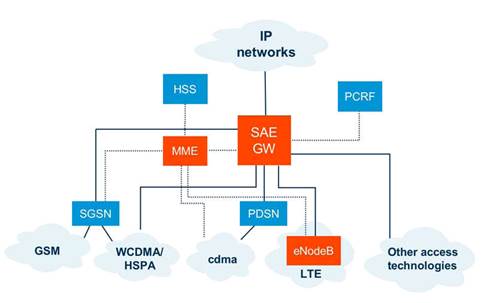
Long
Term Evolution (LTE) is a 3GPP standard that provides uplink speed of up to 50
megabits per second (Mbps) and downlink speed of up to 100 Mbps.
When I met Adrian Scrase, head of Mobile
Competence Centre, 3GPP, in 2011, he told me that when he was in India in 2010
very few people were aware of LTE, and today almost everyone in India is
looking at it as the next very high-speed data technology.
At the 3rd LTE India 2012 International
Conference held in May 2012, Scrase commented, "LTE was a dream for the
Indian operators, but today releasing the growth and the level of satisfaction
required, LTE has become a reality in India with Airtel launching their
services first in Kolkata in April and subsequently in Bengaluru in May 2012”.
LTE - a
multi-frequency technology
One thing unique about LTE is that the
standard can be used with several different frequency bands. This means that
operators can deploy it at lower frequencies with better propagation
characteristics, since the lower the frequency, the lower are the losses.
The 3GPP standard lists as many as 20
different frequency bands for frequency-division duplex (FDD) LTE, with another
nine bands for time- division duplex (TDD) LTE. Operators around the globe are
beginning to reap the benefit of LTE's spectrum flexibility. The broadband
wireless access (BWA) spectrum in India is one 20MHz block of the spectrum (per
operator per circle). This implies that the same spectrum shall be used for
sending or receiving data and hence it is called TDD spectrum. In contrast,
2.1GHz FDD 3G spectrum assignments comprise a 5MHz component for sending and a
separate 5MHz component for receiving wireless transmissions. India went in for
TDD mode as it could not afford to use a large frequency band that FDD calls
for.
TDD spectrum has certain advantages and
some shortcomings too. Operators may choose to use the spectrum in a downlink-
(users receiving data) or uplink-intensive mode, depending on the nature of
popular applications in their networks. For example, if most users download a
lot of video clips frequently but upload only occasionally, operators may use
the spectrum in a configuration that favors downlink transmissions.
FDD spectrum allows no such flexibility;
in the above example, the uplink portion of the spectrum is effectively wasted.
There is a cost, however, in TDD mode wherein there needs to be a guard period
between downlink and uplink transmissions.
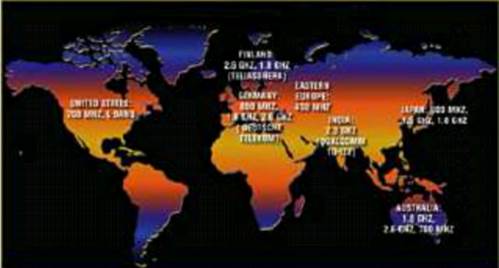
LTE
around the world
TeliaSonera has launched LTE in Finland's
2.6GHz band and will expand the services at 1.8 GHz. Six operators in Eastern
Europe have applied to the International Telecommunications Union to deploy
LTE in the re-farmed 450MHz spectrum presently being used for CDMA. Deutsche
Telekom is looking to deploy LTE in 800MHz, 1.8GHz and 2.6GHz bands in Germany.
In Japan, LTE deployments are in 800MHz,
1.5GHz and 1.8GHz bands, while Verizon is using the 700MHz LTE network in the
United States.
The device and chipset issue
While the capacity to launch LTE in a wide
gamut of spectrum bands has advantages, it brings the baggage of complications
for chipmakers and device manufacturers. Which frequencies will be used by
operators is a big question today as it will significantly impact costs, vendor
margins, time to market and distribution, create technical challenges for
global roaming and inhibit decision-making process within the operator community.
It is important for chipset manufacturers and OEMs such as Qualcomm, Altair
and Broadcom to understand the operator demand for LTE deployments by band so
that they can then produce them on a large scale.
From the table given here, it is evident
that a considerably larger number of devices, including dongles, routers, smartphones
and tablets, are available on LTE-FDD, and more so in the 700MHz band, due to
adoptability of the same in the US market. The LTE ecosystem is evolving at
great speed with 347 LTE devices launched by 63 manufacturers available in the
market as of April 2012.
Increased spectrum efficiency
Spectral efficiency is the information rate
that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication
system. It is a measure of how efficiently a limited frequency spectrum is
utilized by the physical-layer protocol, and sometimes by the media access
control (channel access protocol).
The LTE system can be scaled from 1.4 to 20
MHz; 1.4 MHz, 3 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz, 15 MHz and 20 MHz wide cells are
standardized. This means that apart from being able to operate in various
frequency bands, it also promises scalable bandwidth. Networks can be launched
with a small amount of spectrum, alongside existing services, and more spectrum
can be added as the number of subscribers grows. It also enables operators to
customize their network deployment as per their needs and available spectrum
resources rather than being forced to make their spectrum fit a certain
technology.
LTE can be deployed in clear spectrum with
bandwidth as wide as 20 MHz of paired spectrum (20MHz uplink, 20MHz downlink).
Paired spectrum is two equal parts of airwaves - one for sending and the other
for receiving information - while unpaired spectrum is only a single part of
airwaves meant to either receive or send information. Voice signals travel over
paired spectrum, while data communication works better on unpaired spectrum as
people download more than upload.

4G
LTE single-mode modem by Samsung, operating in the first commercial 4G network
by Telia
The high bandwidth of a single-carrier
radio delivers superb economies of scale vis-a-vis multi-radio legacy
approaches. It also provides scope for considerably bigger capacity than
3G-3.5G technologies that are limited to 5MHz or smaller spectrum bandwidth. It
must be noted that since LTE uses wider chunks of spectrum, data transfer on
LTE-based 4G networks is nearly four times faster than on 3G. LTE with its
spectrum flexibility has a good life ahead since it can be accommodated into
many different swathes of spectrum.