Installing Powershell
The most important thing that needs to be done
before PowerShell can be used is to make sure it is installed, and if
it is not, you need to download and install it. If you have Windows 7
or Windows Server 2008 R2, then you do not have to do anything. They
both include PowerShell 2.0. If you do not have Windows 7 or Windows
Server 2008, however, then you will most likely need to download and
install PowerShell yourself. Installing PowerShell is simple, but
first, you will check to see if it is already there. By far, the
easiest way to check is to open a run window. You do this by clicking
on the start menu → run. This will bring up a dialogue box, now type PowerShell
and hit enter. If a command window comes up, then you have PowerShell.
Now, you check to see if you have the latest version. The easiest way
is to run PowerShell, and then when the shell comes up, you type Get-help about_Windows_PowerShell_2.0.
If the command runs, then you have PowerShell
version 2.0. If you do not have PowerShell at all or if you do not have
the latest version, then you need to go and install it.
Before you install it, you
need to make sure that the minimum system requirements are met. WinRM
2.0 and Windows PowerShell 2.0 can be installed on the following
operating systems:
Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2
Windows XP with Service Pack 3
Windows Vista Service Pack 1 or later
In addition, Windows PowerShell requires the .NET
framework with service Pack 1 to function, so that needs to be
installed as well.
The recommended steps are as follows:
1. | Uninstall previous versions of Windows PowerShell from your computer.
|
2. | Uninstall previous versions of WinRM from your computer.
|
3. | Download and install the latest version of PowerShell 2.0 from http://support.microsoft.com/kb/968929
|
Introduction to Powershell Scripting
The mere mention of the word “scripting” sends many
brave administrators running for the hills. Brave souls immediately
pick up the phone and call their programmer friend. It does not have to
be this way. PowerShell scripting is easy to grasp. In addition,
PowerShell has easy help available for anything you need to use. I am
not talking about online help, but built in, though it does have an
online help option now in version 2.0 as well. Once you have PowerShell
installed on your system, just open and run it. A window that looks a
lot like a dos window should pop up. Now, you will type in a command.
The way you issue commands to PowerShell is to type in a command and
then hit enter. A commandlet or cmdlet is basically a windows
PowerShell command. cmdlets are what allow you to accomplish what you
want with PowerShell. All cmdlets follow a specific naming convention
of “verb-noun” which makes them easier to learn and use.
The most important cmdlet in PowerShell is get-help.
This cmdlet alone can get you the tools you need to get out of any
bind. You can type Get-help followed
by any PowerShell cmdlet to get some meaningful information about them.
An alternative to the get-help cmdlet is the man command. It behaves
just like the get-help cmdlet but will pause the screen for you and display a page at a time instead of displaying all the information at once.
To make sure you are ready to execute cmdlets, run
scripts, and import modules in PowerShell, you want to make sure that
your execution policy will let you run the cmdlets that you need. By
default, the execution policy is set to restricted. You need to set it
to RemoteSigned at the very least. RemoteSigned will allow you to run
any script you write as well as any downloaded script that has been
signed by a trusted publisher. The way you check your execution policy
using the Get-ExecutionPolicy cmdlet is as follows:
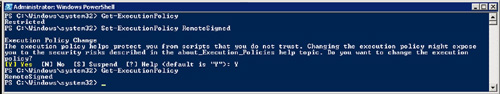
Startup PowerShell as administrator. You will need to have administrator rights to change the execution policy.
Type Get-ExecutionPolicy.
This command should return your current execution policy which will, by
default, be Restricted. Your goal is to change it to RemoteSigned.
Type Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned. When the cmdlet runs, it will give you a warning that you are changing the Execution Policy and a confirmation dialogue (see Figure 1).
The default is Yes, so just hit enter. Voila, you have just changed
your execution policy to RemoteSigned. You can verify this by typing Get-ExecutionPolicy
at the PowerShell prompt. Your new execution policy should show up as
RemoteSigned if you did everything properly and this means that you are
ready to proceed.
PowerShell lets you write cmdlets one line
at a time and hit enter just like a command line shell, but one of the
main advantages is the ability to write scripts. Throughout these
sections, you will see several steps illustrating how something is
done. Everything is done in a step-by-step manner simply for
illustration purposes. All these things could have been done by writing
them in a text file, naming the file with a .ps1 extension, and simply
calling the file. The file would be treated as if you were typing all
the cmdlets in at the
prompt. This is one of the biggest advantages of PowerShell. You write
it once and then can use it multiple times whenever you need it. This
eliminates the human error inherent in mindless repetition as well as
making it easier to share solutions with other administrators.