The following sections describe each of the
Group Policy Preferences settings that fall under the Computer
Configuration and User Configuration sections. If the setting falls
under only one section, that is specified. If nothing is mentioned, the
setting appears under both sections.
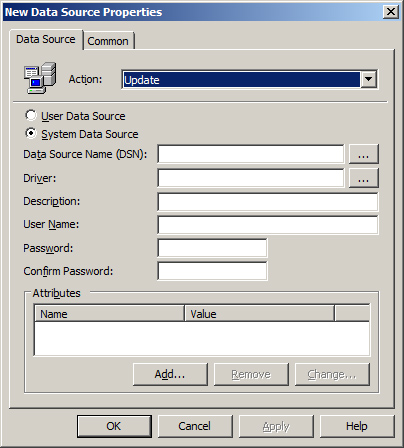
Data Sources
The
Data Sources preference provides a way to centralize the configuration
of Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) data sources. The data sources can
be created, replaced, updated, and deleted for both users and
computers. Figure 1 illustrates the interface for the Data Sources preference and the options that can be configured.
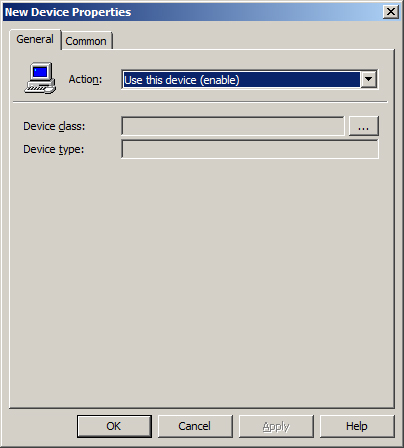
Devices
The
Devices preference allows you to centrally control one or more devices
that connect to the computer. You can enable or disable devices,
including USB ports, floppy drives, removable media, and more, by using
this preference. For this policy setting to function properly, the
device must be active on the computer. This policy setting does not
control devices or prevent devices from being installed. Figure 2 illustrates the interface for the Devices preference and the options that can be configured.
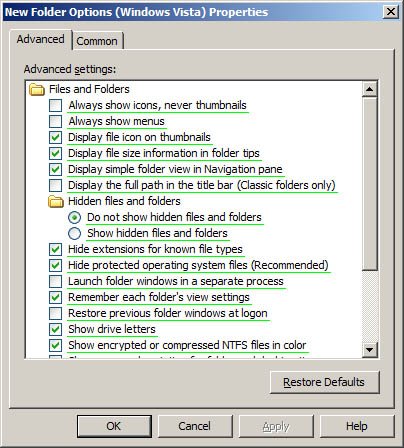
Folder Options
The
Folder Options preference is divided into two parts to control two
types of items. The first part includes the folder options themselves,
which is further split to control settings separately for Windows XP
and Windows Vista. The other part is the Open With configurations,
which control file extensions and the applications that open them. Figure 3 illustrates the interface for the Folder Options preference and the options that can be configured.
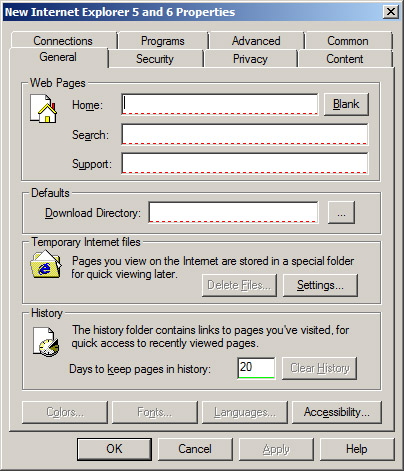
Internet Settings
The
Internet Settings preference provides control over Internet Explorer 5,
Internet Explorer 6, and Internet Explorer 7. Some settings overlap
with the Internet Explorer Maintenance settings, but these preference
settings are not enforced. Figure 4 illustrates the interface for the Internet Settings preference and the options that can be configured.
Note
The Internet Settings preference is available only in the User Configuration section. |
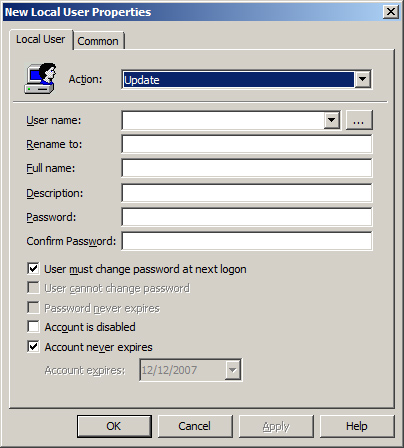
Local Users and Groups
The
Local Users and Groups preference is one of the most powerful and
useful of all of the Group Policy Preferences settings. This preference
can control local accounts on desktops and servers that have joined a
domain. It covers the creation and modification of existing accounts,
including resetting the password for local accounts. This preference
also controls local group accounts, including the membership of the
account. Although seemingly similar to the standard Restricted Groups
policy setting, the Local Users and Groups preference does not “delete
and replace” the group membership. Figure 5 illustrates the interface for the Local Users preference and the options that can be configured.