2.3.9 Wireless Network (IEEE 802.11) Policies (Computer Configuration Only)
This
node provides the ability to configure wireless networks for desktops
running Windows XP or Windows Vista that are joined to the domain. The
options for configuring the wireless network for Windows XP is somewhat
limited compared to those for Windows Vista. The policy for Windows XP
is shown in Figure 12.
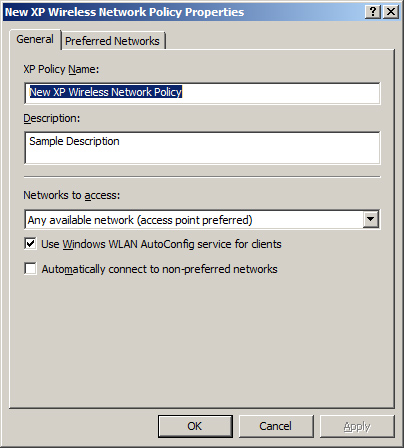
The
policy available to configure desktops running Windows Vista provides
additional setting and configuration options beyond those for desktops
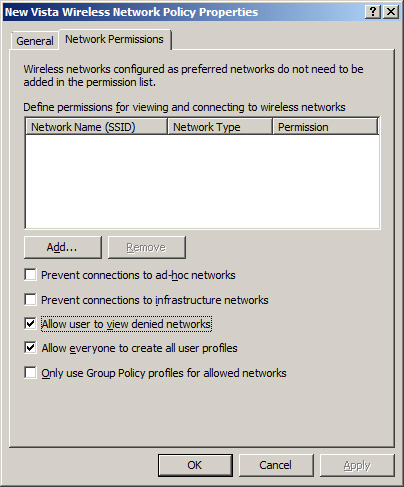
running Windows XP. The policy for Windows Vista is shown in Figure 13. Some of the additional configurations available for Windows Vista include:
Prevent connections to certain types of networks, such as ad-hoc and infrastructure
View denied wireless networks
Create all user profiles
Permissions for wireless networks (allow or deny)
2.3.10 Public Key Policies
The
policies included under this node are designed to configure, control,
and manage the public key infrastructure for your company. The settings
include control over EFS, certificate requests, certificate trust
lists, and certificate authorities. Two of the policies are located under the root node, and the rest are located under one of the following subnodes:
Encrypting File System
Automatic Certificate Request Settings
Trusted Root Certification Authorities
Enterprise Trust
Intermediate Certification Authorities
Trusted Publishers
Untrusted Certificates
Trusted People
2.3.11 Software Restriction Policies
This
node provides you with the ability to control which applications can
run on a desktop that is affected by the GPO where the policies are
configured. These policies do not allow or prevent the software from
existing on the desktop; rather, if the software is present, the
policies determine whether it is allowed to run. This node and its
subnodes contain numerous options for configuration that allow you to
control the software that runs on any desktop in the domain. The
majority of the settings fall under the following two subnodes,
although a few policies are located under the main node:
Security Levels
The security levels control what level of privilege and which
permissions will be adhered to within the software restriction policy.
The following three levels can be configured:
Disallowed: software will not run, regardless of the user permissions and privilege.
Basic
User: allows applications to execute for users who do not have
Administrative privileges, but the application will still access
resources as a normal user.
Unrestricted: the permissions to run the software are determined by the access rights of the user account.
Additional Rules
The additional rules control whether the software is allowed to run.
These rules allow you to be very specific to an application, such as
the hash rule, whereas other rules are more generic, such as the path
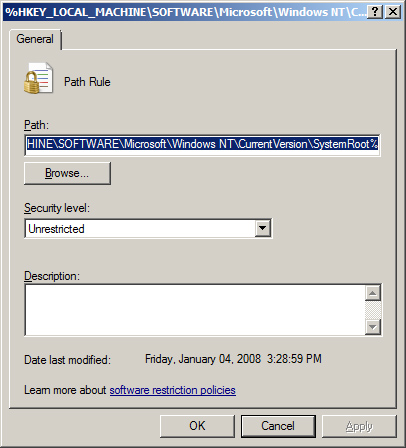
rule. Figure 14 illustrates a path rule policy. Four rules can be configured:
Certificate rule
Hash rule
Network zone rule
Path rule
2.3.12 Network Access Protection (Computer Configuration Only)
These
policy settings control the environment of Network Access Protection
(NAP) for target computers. The settings that fall under this node in a
GPO control which service will quarantine the clients, the NAP
interface details, and which servers will be used for obtaining health
certificates.
Enforcement Clients These policies determine which service or technology will enforce NAP and quarantining of the client. The options include:
DHCP Quarantine Enforcement Client
Remote Access Quarantine Enforcement Client
IPsec Relying Party
TS Gateway Quarantine Enforcement Client
EAP Quarantine Enforcement Client
User Interface Settings This policy simply configures the details that the client will see in the NAP interface.
Health Registration Settings
These settings control the hash algorithms and health registration
authority servers that clients will use to obtain their health
certificates. Two subnodes contain policy settings, which must be
configured to complete the health registration settings:
Request Policy
Trusted Server Groups
2.3.13 IP Security Policies on Active Directory (Computer Configuration Only)
IPsec
is a protocol that can help increase security of data that is
communicated from computer to computer. In most cases, IPsec is used to
protect data communicated over a network that is not secure. IPsec has
many configurations, all of which can be customized. Three policies are
preconfigured and ready to use, if you do not want to customize your
own IPsec policy:
Client (Respond Only)
This policy is intended to be used for computers that will respond to
computers requesting the use of IPsec for data communication. This is
ideal for environments in which IPsec is not used on all servers; but
when it is used on some servers, this policy allows the client to
respond appropriately to the IPsec request.
Secure Server (Require Security) This policy is designed to force a server to use IPsec for all communication.
Server (Request Security)
This policy is designed to be flexible with the use of IPsec. In
essence, the policy will try to use IPsec with all communications, but
when communicating with a downlevel client that does not support IPsec,
it will not cause the communication to fail.
2.3.14 Folder Redirection (User Configuration Only)
When
a computer and user are working within the context of a domain instead
of a workgroup, it is ideal to centralize the data that users utilize
for security, roaming users, and disaster recovery reasons. To
accommodate this environment, the folder redirection policies allow you
to control which user folders store data locally on the user’s hard
drive and which user folders are redirected to a network share, so that
the data can be controlled by the IT staff. The folders that can be
redirected using this policy include:
AppData (Roaming)
Desktop
Start Menu
Documents
Pictures
Music
Videos
Favorites
Contacts
Downloads
Links
Searches
Saved Games
2.3.15 Policy-Based QoS
Quality
of Service (QoS) is a suite of technologies that manage network traffic
to optimize the bandwidth, cost, and overall network constraints. With
QoS policies, you can manage and optimize network traffic when network
conditions change and become congested to ensure that applications
function optimally.
2.3.16 Internet Explorer Maintenance (User Configuration Only)
The
policies located under this node and its subnodes are designed to
configure, control, and secure many aspects of Microsoft Internet
Explorer. In some cases, you will use the settings that are set on the
computer that is performing the editing of the GPO to configure the
policies; in other cases, you can make manual entries to the policy
settings. The result is a suite of Internet Explorer settings stored in
the GPO that is deployed to all users who fall under SOM of the GPO.
The subnodes of policy settings that fall under this node include the
following:
Browser User Interface This node of policies is designed to configure the interface to Internet Explorer. Three policies fall under this subnode:
Connection
Many settings are associated with Internet Explorer when a unique or
specific connection must be made to access the Internet. The settings
in this node can help you make the appropriate configurations to ensure
connectivity. Four policies fall under this node:
URLs
You can help users in your environment to be more productive and
efficient by providing them with URLs to locations that are important
to them. Two types of URLs can be configured under this policy node:
Favorites and Links
Important URLs
Security
You can use this policy to establish the security zones, content
ratings, and Authenticode settings for Internet Explorer. These
settings can be ignored by the GPO processing or imported from the
computer performing the editing of the GPO.
Programs
You can configure Internet Explorer to use specific programs to control
the HTML editor, E-mail, Newsgroups, Internet calls, Calendar, and
Contact list. This policy can be configured by importing the local
Internet Explorer settings from the editing computer.